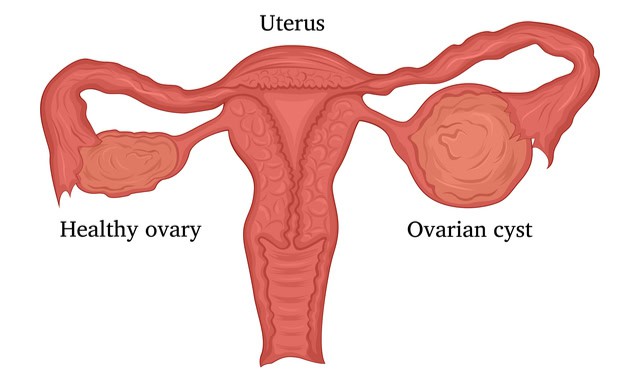
The ovaries are an integral part of the female reproductive system. It plays a key role in the production of eggs and hormones namely estrogen and progesterone. In some cases, sacs filled with fluid develop in or on the ovary, which is clinically known as ovarian cysts. These can occur in women of all ages, however, women in the reproductive age group are at a higher risk as compared to older women. Some women with ovarian cysts may experience symptoms while in some, it may have no symptoms as the cysts are painless.
In most cases, these cysts might need no treatment as they do not interfere with the normal body processes. However, in some, these can grow in size and can interfere with the ovarian function and cause symptoms. In rare cases, these cysts can also lead to cancer. In this article, we shed some light on the causes, types, and symptoms of ovarian cysts every woman needs to be aware of.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are various types of ovarian cysts, but the most common cysts are corpus luteum and follicle cysts.
Follicle Cyst: During menstruation, an egg, which is grown in a sac-like structure known as a follicle, is released by the ovaries. In most cases, the follicle breaks open to release the egg. But in some cases, the follicle does not break which causes the fluid inside the follicle to form a cyst.
Corpus Luteum Cyst: When a follicle releases the egg, the structure is known as corpus luteum. But if the sac seals again after releasing the egg in the ovary, it causes accumulation of the fluid in the surrounding areas which causes a cyst.
Other types of cysts are endometriomas, dermoid cyst, and cystadenomas[1].
Dermoid Cyst: This type of cyst contains hair, fat and other tissue which grow on the ovaries.
Cystadenomas: As the name suggests, these are noncancerous growths that develop on the surface of the ovaries.
Endometriomas: When the cyst is formed from the uterine tissue but attaches itself on the ovaries, it is known as endometriomas.
Browse Our Range Of Feminine Hygiene And Care Products.
Ovarian Cyst: Symptoms
Not all cysts cause any noticeable symptoms, but you may experience symptoms if the cysts continue growing. The effects of ovarian cyst symptoms are not limited to the lower abdomen only and can cause discomfort in various ways. The symptoms of ovarian cysts are:
– Bloating of the abdomen
– Swelling or pain in the lower abdomen
– Aching thighs or lower back
– Heightened pain during or before the menstrual cycle
– Fever, vomiting, and nausea
Benign vs. Malignant Ovarian Cysts
Based on the symptoms, ovarian cysts are classified into two broad categories: benign cysts and malignant cysts[2]. Benign cysts are functional cysts and not cancerous. The second type of cyst is known as malignant cysts which are rare and cancerous in nature.
Benign Cysts
Benign cysts are noncancerous cysts and are unable to spread throughout the body. These cysts are characterized by abnormal tissue growth which is formed during the menstrual cycle. Benign cysts are often surrounded by a protective ‘sac’ that segregates itself from the rest of the body. These cysts can be caused due to genetics, stress, diet, and exposure to radiation.
Benign ovarian cysts treatment is not needed unless they press on vital structures such as blood vessels or nerves or are leading to some symptoms. Surgery which will help to remove the cysts from the ovaries is recommended if the condition becomes severe or interferes with the person’s day-to-day activities.
Malignant Cysts
Malignant cysts are cancerous and rare. Cancerous cysts indicate ovarian cancer and are more common in older women[3]. A cyst is suspected to be malignant when specific characteristics are observed during a physical exam, ultrasound or in a patient’s medical history. This type of cyst can spread to various parts of the body and can multiply uncontrollably. Malignant cysts can be treated with surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy or a combination of these as per disease status and clinical advice.
What Causes Ovarian Cysts?
There are several factors which can cause ovarian cysts. Some of the common ones are:
Hormonal problems: Functional cysts, which are also known as benign cysts, can be caused due to hormonal changes in the body. For example, women taking hormonal pills or drugs used to ovulate can also cause hormonal changes.
Endometriosis: It a painful condition in which the tissue that lines the uterus (known as the endometrium), grows outside the uterus. If you are suffering from endometriosis, there are chances that you might develop endometrioma, a type of ovarian cyst in which the cyst of the endometrial lining goes and attaches to the ovaries.
Severe pelvic infection: In some cases, the infection of the pelvic region can spread to the ovaries and fallopian tubes. This can trigger a formation of cysts on the ovaries leading to ovarian cysts.
**Consult India’s best doctors here**
Can Ovarian Cysts Be Prevented?
You cannot prevent ovarian cysts. However, routine gynecologic tests can detect early-stage ovarian cysts as the symptoms are not seen in some cases. It is advisable to visit a doctor once every three months for check-ups or visit your doctor immediately if you experience any symptoms such as severe pain in the pelvic region, swelling in the lower abdomen or nausea and vomiting accompanied with pain.
Your doctor might do a routine pelvic examination and order imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI or CT scan to diagnose ovarian cysts. In some cases, additional tests such as a pregnancy test (to rule out pregnancy), hormonal test (to check the level of estrogen and progesterone) and CA-125 marker test (to screen ovarian cancer) might be recommended. Based on the severity and the type of ovarian cysts, your doctor might advise medications (hormonal pills to control the growth of the cyst) and/or surgery (to remove cysts).
(The article is reviewed by Dr. Lalit Kanodia, General Physician)
Recommended Reads:
Common Causes Of Pelvic Pain In Women
UTI Infection In Women: 8 Common Questions Answered!
References:
1. Publishing H. Cysts (Overview) – Harvard Health [Internet]. Harvard Health. 2018 [cited 14 September 2018].
2. Ovarian cyst [Internet]. NHS.UK. 2018 [cited 14 September 2018].
3. Sundar S, Neal RD, Kehoe S. Diagnosis of ovarian cancer. BMJ. 2015 Sep 1;351(5):1283-95.