
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the world [1]. Out of many lifestyle habits, following a heart-healthy diet is one of the most effective ways to reduce your risk of heart disease. The Mediterranean diet – consisting of fish, unsaturated fats, whole grains, fruits and vegetables, nuts and legumes – has consistently been shown to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality [1].
Not only does the Mediterranean diet lower the risk of heart disease, but it also reduces the risk of many other chronic conditions. A dietitian can help you customize the diet that suits you best.
What is a Mediterranean Diet?

As the name suggests, it arose from the countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It was found out that people living in some Mediterranean countries, such as Greece and Italy, had lower death rates due to cardiovascular diseases.
The Mediterranean way of eating promotes whole, natural, plant-based foods that support overall well-being. Today, the Mediterranean diet is recognized by the World Health Organization and the American Heart Association as a healthy dietary pattern that emphasizes vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans, and legumes; includes low-fat dairy, fish, poultry, vegetable oils, and nuts; and limits added sugars, sodium, refined carbs, saturated fats, and processed foods [2].
Mediterranean Diet For Heart Health

So, how exactly does the diet help in better heart health and overall longevity? Let’s explore 5 science-backed benefits of the Mediterranean diet for heart health and a healthier, longer life.
1. Reduces the Risk Of Heart Diseases

Studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease. With healthy fats from olive oil and nuts as key components, people following this diet had up to a 30% reduced risk of major heart events compared to those on a low-fat diet. These healthy fats help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol, reducing arterial plaque buildup [3].
2. Supports Healthy Blood Pressure
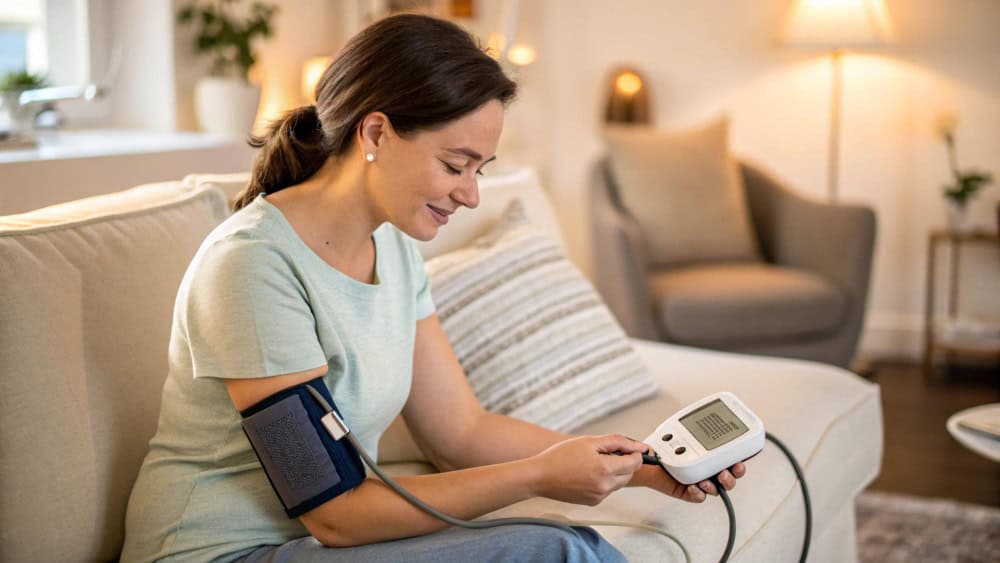

High sodium consumption is linked to high blood pressure, which can cause various heart-related health issues [4]. Switching to the Mediterranean diet not only emphasizes heart-healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and healthy fats but also helps reduce sodium intake. Low-sodium salts replace some sodium with potassium, lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease [5].
3. Lowers Bad Cholesterol Levels
With healthy fats such as extra virgin olive oil, avocados, and nuts, which help increase HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol), the Mediterranean diet is considered one of the best diets to reduce LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol that clogs arteries). This is how, by keeping the cholesterol levels in check, this diet keeps your arteries clear and lowers the risk of atherosclerosis, a major cause of heart attacks and strokes.
4. Helps Maintain a Healthy Weight

Obesity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce this risk [6]. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, high-fibre vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, and minimizing processed items, the diet promotes satiety, encourages portion control, and supports gradual, sustainable weight loss. Unlike restrictive diets, it allows flavourful, satisfying meals while helping lower the risk of heart disease associated with obesity.
5. Improves Overall Longevity and Quality of Life

The benefits of the Mediterranean diet extend beyond just lowering risks. It helps people live longer and healthier lives. Combining balanced nutrition with lifestyle aspects such as shared meals, moderate physical activity, and mindful eating, this diet creates a holistic approach to well-being. People who follow this diet consistently are less likely to develop not just heart disease but also other chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and certain cancers.
Final Takeaway
Making the switch to the Mediterranean diet doesn’t have to be overwhelming – start with small steps like replacing butter with olive oil or adding more vegetables to the meal. But before starting a Mediterranean diet plan, it is advised to consult a dietitian or a doctor.
Shop heart care products to complement your Mediterranean diet.
At Tata 1mg, we have come up with an initiative to commit to protecting your heart.
Take a pledge; you are just a click away.
Disclaimer: This is a sponsored article co-powered by Tata Salt Lite. The information provided in this article, in the form of text, tips, suggestions, and products, comprises general advice for consumers. Tata 1mg does not endorse any brands and is not responsible for their efficacy.
(The article is written by Sneha Jajoo, Intern, Clinical Health & Content, and is reviewed by Dr.Subita Alagh, Assistant Team Lead, Disease Content.)
References
1. Widmer RJ, Flammer AJ, Lerman LO, Lerman A. The Mediterranean diet, its components, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Med. 2015;128(3):229-238. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.10.014
2. American Heart Association. What is the Mediterranean Diet? Available from: https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/nutrition-basics/mediterranean-diet
3. Estruch R, Ros E, Salas-Salvadó J, et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. New England Journal of Medicine. 2018;378(25):e34. doi:10.1056/nejmoa1800389
4. World Health Organization: WHO. Sodium reduction. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sodium-reduction. Published February 7, 2025.
5. Heart Foundation. Salt and heart health. Available online from https://www.heartfoundation.org.au/healthy-living/healthy-eating/salt-and-heart-health
6. World Heart Federation. Obesity and cardiovascular disease. (2022)
FAQs
Q. Does the Mediterranean diet improve heart health?
Yes, studies show that it lowers blood pressure, reduces bad cholesterol, and reduces the overall risk of heart disease.
Q. What are the advantages of the Mediterranean diet?
It supports heart health, longevity, brain health, and weight management, which ultimately lowers the risk of chronic diseases.
Q. What is not allowed on a Mediterranean diet?
Processed foods, red meat, sugary drinks in excess, and highly processed oils are generally avoided.
Recommended Reads:
2025 Blood Pressure Guidelines: Why Are They A Wake-Up Call for Young Adults
