- TOP CITIES
- New Delhi
- Gurgaon
- Pune
- Mumbai
- Bengaluru
- Kolkata
- Hyderabad
- Ahmedabad
- Chennai
- Indore
- Lucknow
- Jaipur
- Chandigarh
- Bhopal
- Noida
- Navi Mumbai
- Surat
- Patna
- Ludhiana
- Bhubaneshwar
- ALL CITIES
- Abohar
- Adilabad
- Adoni
- Agar
- Agartala
- Agra
- Ahmedabad
- Ahmednagar
- Aizawl
- Ajmer
- Akola
- Alappuzha
- Aligarh
- Alipurduar
- Alirajpur
- Allahabad
- Almora
- Alwar
- Ambala
- Ambattur
- Ambedkar Nagar
- Amravati
- Amreli
- Amritsar
- Amroha
- Anand
- Anantapur
- Ananthnag
- Anantnag
- Angamally
- Angul
- Ankleshwar
- Annur
- Anuppur
- Arakkonam
- Arambag
- Arantangi
- Araria
- Arcot
- Ariyalur
- Arwal
- Asansol
- Ashok Nagar
- Assaudh
- Attuvampatti
- Auraiya
- Aurangabad Bihar
- Aurangabad Maharashtra
- Aviyur
- Ayyangarkulam
- Azamgarh
- Badlapur
- Bagalkot
- Bageshwar
- Baghpat
- Bagpat
- Bahadurgarh
- Bahraich
- Baksa
- Balaghat
- Balangir
- Baleswar
- Ballia
- Bally
- Balrampur
- Banaskantha
- Banda
- Bangalore
- Bangalore Rural
- Banka
- Bankura
- Banswara
- Barabanki
- Baramati
- Baramulla
- Baran
- Baraut
- Bardhaman
- Bareilly
- Bargarh
- Barmer
- Barnala
- Barpeta
- Barrackpore
- Baruipur
- Barwani
- Basirhat
- Bastar
- Basti
- Bathinda
- Beawar
- Beed
- Begumganj
- Begusarai
- Behraghora
- Behrampur
- Belgaum
- Bellary
- Belur
- Bengaluru
- Betul
- Betul Ganj
- Bhadrak
- Bhadravati Karnataka
- Bhagalpur
- Bhandara
- Bharatpur
- Bharuch
- Bhatkal
- Bhavani
- Bhavnagar
- Bhilai
- Bhilwara
- Bhind
- Bhiwadi
- Bhiwandi
- Bhiwani
- Bhojpur
- Bhopal
- Bhubaneshwar
- Bhuna
- Bhusawal
- Bidar
- Bijapur Chattisgarh
- Bijapur Karnataka
- Bijnor
- Bikaner
- Bilaspur Chattisgarh
- Bilaspur Himachal Pradesh
- Birbhum
- Bishnupur
- Boisar
- Bokaro
- Bongaigaon
- Bongaon
- Botad
- Boudh
- Budaun
- Budgam
- Bukkapatnam
- Bulandshahr
- Buldana
- Buldhana
- Bundi
- Burdwan
- Burhanpur
- Buxar
- Cachar
- Calicut
- Chamarajanagar
- Chamba
- Chamoli
- Champawat
- Champhai
- Chandauli
- Chandel
- Chandigarh
- Chandrapur
- Changanassery
- Changlang
- Chatra
- Chennai
- Chhatarpur
- Chhindwara
- Chikkaballapur
- Chikkaballapura
- Chikmagalur
- Chintamani
- Chitradurga
- Chitrakoot
- Chittoor
- Chittorgarh
- Chrompet
- Churachandpur
- Churu
- Cochin
- Coimbatore
- Cooch Behar
- Cuddalore
- Cuddapah
- Cuttack
- Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Dahanu
- Dahod
- Dakshina Kannada
- Daman
- Damoh
- Dantewada
- Darbhanga
- Darjiling
- Darrang
- Datia
- Dausa
- Davangere
- Debagarh
- Dehradun
- Delhi
- Deoghar
- Deoria
- Dera Bassi
- Devanahalli
- Dewas
- Dhakaoli
- Dhalai
- Dhamtari
- Dhanbad
- Dhar
- Dharmapuri
- Dharwad
- Dhemaji
- Dhenkanal
- Dholpur
- Dhone
- Dhubri
- Dhule
- Dhully
- Dibang Valley
- Dibrugarh
- Dibrugarh Tamil Nadu
- Dimapur
- Dindigul
- Dindori
- Dispur
- Diu
- Doda
- Dombivli
- Dombivli Station
- Dumka
- Dungarpur
- Durg
- Durgapur
- East Champaran
- East Garo Hills
- East Godavari
- East Kameng
- East Khasi Hills
- East Midnapore
- East Nimar
- East Siang
- East Sikkim
- East Singhbhum
- Ellanaickenpatti
- Ernakulam
- Erode
- Etah
- Etawah
- Faizabad
- Faridabad
- Faridkot
- Farrukhabad
- Fatehabad
- Fatehgarh Sahib
- Fatehpur
- Fazilka
- Firozabad
- Firozpur
- Gadag
- Gadarwara
- Gadchiroli
- Gajapati
- Gandhinagar
- Ganganagar
- Gangtok
- Ganjam
- Garhwa
- Gariaband
- Gautam Buddha Nagar
- Gaya
- Ghaziabad
- Ghazipur
- Gir Somnath
- Giridh
- Goa
- Goalpara
- Gobichettipalayam
- Godda
- Golaghat
- Golaniya
- Gonda
- Gondia
- Gopalganj
- Gorakhpur
- Greater Noida
- Greater Thane
- Gulbarga
- Gumla
- Guna
- Guntur
- Gurdaspur
- Gurgaon
- Guwahati
- Gwalior
- Hailakandi
- Halol
- Hamirpur Himachal Pradesh
- Hamirpur Uttar Pradesh
- Hansi
- Hanumangarh
- Hapur
- Harapanahalli
- Harda
- Hardoi
- Haridwar
- Hassan
- Hathras
- Haveri
- Hazaribag
- Hazaribagh
- Hinauti
- Hindaun
- Hingoli
- Hisar
- Hojai
- Hooghly
- Hosakote
- Hoshangabad
- Hoshiarpur
- Hoskote
- Hospet
- Hosur
- Howrah
- Hubli
- Hyderabad
- Ichalkaranji
- Idukki
- Imphal
- Imphal East
- Imphal West
- Indore
- Itanagar
- Jabalpur
- Jagatsinghapur
- Jaintia Hills
- Jaipur
- Jaisalmer
- Jajapur
- Jalandhar
- Jalaun
- Jalgaon
- Jallipatti
- Jalna
- Jalore
- Jalpaiguri
- Jammu
- Jamnagar
- Jamshedpur
- Jamtara
- Jamui
- Janjgir-Champa
- Jashpur
- Jaunpur
- Jayamala
- Jehanabad
- Jhabua
- Jhajjar
- Jhalawar
- Jhansi
- Jhargram
- Jharsuguda
- Jhujhunu
- Jind
- Jodhpur
- Jorhat
- Junagadh
- Jyotiba Phule Nagar
- Kachchh
- Kadamakkudy
- Kadapa
- Kadiri
- Kadthal
- Kaghaz Nagar
- Kaimur Bhabua
- Kaithal
- Kakinada
- Kalahandi
- Kalipahari
- Kallakurichi
- Kalligudi
- Kalyani
- Kamrup
- Kanadukathan
- Kanchipuram
- Kandhamal
- Kandukur
- Kangra
- Kanker
- Kannauj
- Kannur
- Kanpur
- Kanpur Dehat
- Kanpur Nagar
- Kansapuram
- Kanyakumari
- Kapurthala
- Karad
- Karaikal
- Karaikudi
- Karatholuvu
- Karauli
- Karbi Anglong
- Kargil
- Karimganj
- Karimnagar
- Karnal
- Karupatti
- Karur
- Karwar
- Kasaragod
- Kathua
- Katihar
- Katni
- Kattupakkam
- Kaushambi
- Kavaratti
- Kawardha
- Kendrapara
- Kendujhar
- Khagaria
- Khammam
- Khandwa
- Khanna
- Kharagpur
- Khargone
- Kheda
- Kheri
- Khorda
- Kichha
- Kinnaur
- Kiphire
- Kishanganj
- Kochi
- Kodagu
- Kodaikanal Observatory
- Koderma
- Kohima
- Kokrajhar
- Kolar
- Kolasib
- Kolhapur
- Kolkata
- Kollam
- Kooram
- Koppal
- Koraput
- Korba
- Koriya
- Kota
- Kothakudi
- Kothur
- Kottayam
- Kovilpatti
- Koyilandy
- Kozhikode
- Krishna
- Krishnagiri
- Kulgam
- Kullu
- Kumbakonam
- Kumburvayal
- Kundli
- Kupwara
- Kurnool
- Kurukkalpatti
- Kurukshetra
- Kurung Kumey
- Kushinagar
- Kutch
- Laddivadi
- Lahul & Spiti
- Lakhimpur
- Lakhisarai
- Lakshadweep
- Lalitpur
- Lambakheda
- Latehar
- Latur
- Lawngtlai
- Leh
- Lohardaga
- Lohit
- Lonavala
- Longleng
- Lower Dibang Valley
- Lower Subansiri
- Lucknow
- Ludhiana
- Lunglei
- Machur
- Madhepura
- Madhubani
- Madhupur
- Madikeri
- Madurai
- Mahabubabad
- Mahabubnagar
- Mahadanapuram
- Maharajganj
- Mahasamund
- Mahbub Nagar
- Mahe
- Mahendragarh
- Mahoba
- Mainaguri
- Mainpuri
- Majuli
- Malappuram
- Malda
- Malkangiri
- Malout
- Mammit
- Manakudi
- Manapparai
- Manawar
- Mandi
- Mandi Gobindgarh
- Mandla
- Mandsaur
- Mandya
- Mangalore
- Manipal
- Mannargudi
- Mansa
- Margao
- Marigaon
- Mathura
- Mau
- Mayurbhanj
- Medak
- Meenkashipuram
- Meerut
- Mehsana
- Melaparuthigudi
- Melpallam
- Melpattamkarisalkulam
- Melvisharam
- Midnapore
- Mirzapur
- Moga
- Mohali
- Mohanur
- Mokokchung
- Mon
- Moradabad
- Morena
- Muchipara
- Mughal Sarai
- Muktsar
- Mumbai
- Mumbai Extension
- Munger
- Murshidabad
- Muzaffarnagar
- Muzaffarpur
- Mysore
- Nabarangapur
- Nadia
- Nadiad
- Naduvakurichi
- Nagaon
- Nagapattinam
- Nagaur
- Nagpur
- Naidupuram
- Nainital
- Najibabad
- Nalanda
- Nalbari
- Nalgonda
- Namakkal
- Nanded
- Nandurbar
- Narayanpur
- Narmada
- Narnaul
- Narsinghpur
- Narsipatnam
- Nashik
- Navi Mumbai
- Navsari
- Nawada
- Nawanshahr
- Naxalbari
- Nayagarh
- Neemrana
- Neemuch
- Nelamangala
- Nellore
- Nerur
- New Delhi
- Nicobar
- Nilgiri
- Nilgiris
- Nizamabad
- Noida
- North 24 Parganas
- North And Middle Andaman
- North Cachar Hills
- North Dinajpur
- North Goa
- North Sikkim
- North Tripura
- Nowda
- Nuapada
- Nuh
- Nuvem
- Ooty
- Osmanabad
- Pakur
- Palakkad
- Palamalai
- Palamu
- Palani
- Palghar
- Pali
- Pambakovil Shandy
- Panaji
- Panchkula
- Panchmahal
- Panipat
- Panna
- Panvel - Station
- Papanasam
- Pappankulam
- Pappinaickenpatti
- Papum Pare
- Paradip
- Parbhani
- Pasumpon
- Patan
- Pathanamthitta
- Pathankot
- Patiala
- Patna
- Pauri Garhwal
- Pavitram
- Perambalur
- Peren
- Phalghat
- Phek
- Pilani
- Pilibhit
- Pinnathur
- Pithoragarh
- Pondicherry
- Ponga
- Poonamalle
- Poonch
- Porbandar
- Port Blair
- Prakasam
- Pratapgarh
- Proddatur
- Pudukkottai
- Pulankurichi
- Pulavadi
- Puludipatti
- Pulwama
- Pune
- Pungamuthur
- Purba Bardhaman
- Purbasthali
- Puri
- Purnia
- Puruliya
- Puzhal
- Quilon
- Raebareli
- Raichur
- Raigad Maharashtra
- Raigarh Chattisgarh
- Raikasba
- Raipur
- Raisen
- Rajahmundry
- Rajauri
- Rajgangpur
- Rajgarh
- Rajkot
- Rajnandgaon
- Rajpura
- Rajsamand
- Ramanagar
- Ramanathapuram
- Ramgarh
- Rampur
- Ranchi
- Rangareddi
- Rangareddy
- Ranipet
- Ratlam
- Ratnagiri
- Raurkela
- Rayagada
- Reasi
- Rewa
- Rewari
- Ri Bhoi
- Rishikesh
- Rohtak
- Rohtas
- Roorkee
- Ropar
- Rourkela
- Rudraprayag
- Rudrapur
- Rupnagar
- Rurka Kalan
- S.A.S. Nagar
- Sabarkantha
- Sagar
- Saharanpur
- Saharsa
- Sahibganj
- Saiha
- Salem
- Samastipur
- Sambalpur
- Sambhal
- Sangareddy
- Sangli
- Sangrur
- Sant Kabir Nagar
- Sant Ravidas Nagar
- Saran
- Satara
- Satna
- Sawai Madhopur
- Secunderabad
- Sehore
- Senapati
- Seoni
- Seraikela-Kharsawan
- Serchhip
- Shahapur
- Shaharanpur
- Shahdol
- Shahjahanpur
- Shahpura
- Shajapur
- Shamshabad
- Sheikhpura
- Sheohar
- Sheopur
- Shikohabad
- Shillong
- Shimla
- Shimoga
- Shivpuri
- Shrawasti
- Shyamnagar
- Sibmandir
- Sibsagar
- Siddharthnagar
- Sidhi
- Sihora
- Sikar
- Siliguri
- Silvassa
- Simdega
- Simga
- Sindhudurg
- Singrauli
- Sirkaali
- Sirmaur
- Sirohi
- Sirsa
- Sitamarhi
- Sitapur
- Sivaganga
- Sivakasi
- Sivasagar
- Siwan
- Solan
- Solapur
- Sonapur
- Sonarpur
- Sonbhadra
- Sonipat
- Sonitpur
- Soro
- South 24 Parganas
- South Andaman
- South Dinajpur
- South Garo Hills
- South Goa
- South Sikkim
- South Tripura
- Sricity
- Srikakulam
- Srinagar
- Subarnapur
- Sujangarh
- Sultanpur
- Sundergarh
- Supaul
- Surat
- Surendranagar
- Surguja
- T Pudupatti
- Tadipatri
- Talasari
- Tamenglong
- Tapi
- Tarn Taran
- Tawang
- Tehri Garhwal
- Tenkasi
- Thane
- Thanjavur
- The Dangs
- Theni
- Thimmarajanpettai
- Thirukkalukundram
- Thirukkannamangaikottam
- Thiruvaiyaru
- Thiruvarur
- Thoothukudi
- Thoubal
- Thrissur
- Thungavi
- Tikamgarh
- Timarni
- Tinsukia
- Tirap
- Tiruchendur
- Tiruchirappalli
- Tiruklalikundram
- Tirumani
- Tirunelveli
- Tirupati
- Tiruppur
- Tirupur
- Tirur
- Tiruttani
- Tiruvalla
- Tiruvallur
- Tiruvannamalai
- Tiruvarur
- Titilagarh
- Tohana
- Tonk
- Trimulgherry
- Trivandrum
- Tuensang
- Tumkur
- Turaiyur Koitpatti
- Tuticorin
- Udaipur Rajasthan
- Udaipur Tripura
- Udayarpalayam
- Udham Singh Nagar
- Udhampur
- Udupi
- Ujjain
- Ukhrul
- Umaria
- Una
- Unnao
- Upper Siang
- Upper Subansiri
- Uttara Kannada
- Uttarkashi
- Vadagarai
- Vadakara
- Vadodara
- Vaishali
- Valsad
- Vandavasi
- Vapi
- Varanasi
- Vattur
- Vellore
- Vidisha
- Vijayawada
- Vikarabad
- Villupuram
- Virudhunagar
- Visakhapatnam
- Visalakshi Nagar
- Vizianagaram
- Warangal
- Wardha
- Washim
- Wayanad
- West Champaran
- West Garo Hills
- West Godavari
- West Kameng
- West Khasi Hills
- West Midnapore
- West Nimar
- West Siang
- West Sikkim
- West Singhbhum
- West Tripura
- Wokha
- Y.S.R.
- Yadgir
- Yamunanagar
- Yavatmal
- Zunhebotto
Want to know more?
Read Our Editorial PolicyHave issue with the content?
Report Problem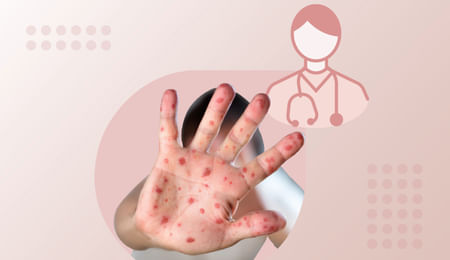
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Also known as HFMD, HFM disease, enteroviral vesicular stomatitis and coxsackievirus infectionOverview
Does your child have fever, mouth ulcers/sores along with rashes on the hand and feet or he/she is reluctant to eat even his/her favorite food? Well, this can be due to a viral infection called the hand, foot, and mouth disease(HFMD) which is very common in children under 5 years of age. It is most commonly seen during summer and autumn seasons.
HFMD is highly contagious that can spread through direct contact with the skin, nasal and oral secretions of infected individuals, or by fecal contamination. The illness usually starts with a high grade fever that is followed by painful mouth ulcers. The characteristic non-itchy rashes on the hands and feet start appearing at last.
HFMD is generally a mild and self-limited illness that runs its course. Treatment is mostly directed toward the relief of symptoms.
Key Facts
- Hand
- Foot
- Mouth
- Enteroviruses
- Erythema multiforme
- Herpangina
- Herpes simplex
- Herpes zoster
- Kawasaki disease
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis(TEN)
- Viral pharyngitis
- Physical examination
- Biopsy
- Serological testing
- Polymerase chain reaction
- General physician
- Pediatrician
- Infectious disease specialist
Symptoms Of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is mostly a childhood illness though it can affect adults also. The symptoms are usually the same in children and adults. But, the disease can be worse in infants and children due to their inability to express their symptoms.
The disease is mild, resembling a common cold in the initial days of infection. In most cases, symptoms last for 7-10 days.
As the name suggests, symptoms appear on the hand, foot and mouth in the form of sores, blisters and rashes. The typical symptoms of HFMD can be broadly classified as:
Fever and flu-like symptoms
These symptoms start appearing after 3 to 5 days of catching the virus. The symptoms include:
-
High fever
-
Loss of appetite
Mouth ulcers
Children suffering from HFMD usually develop mouth sores after a few days of infection. Ulcers appear in the mouth and tongue which gradually progress into painful blisters. This makes swallowing difficult which can be identified by the following signs in children:
-
Not eating even his/her favorite food
-
Drooling (drooping saliva from mouth more than usual)
-
Crying while eating
-
Interest only in having cold fluids
Skin rashes
A child having HFMD gets rashes on the skin which look like slightly raised red spots. The spots can also look pink or darker skin depending upon the skin tone.
The most common sites of rashes are hands and feet, although they can also appear on the buttocks, legs, and arms.
In most of the cases, rashes do not cause itching. Sometimes, rashes develop into blisters which are filled with fluid containing viruses.
Other symptoms
A child with HFMD might also experience
-
Muscles aches
-
Irritability
-
Pain in abdomen
-
Diarrhea
-
Runny nose
-
Peeling of the skin
-
Tenderness or pain while touching the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
-
Vomiting
Here are some important things to remember when your child has one or multiple episodes of vomiting.
Signs of dehydration
The child suffering from HFMD can be dehydrated due to inability to drink anything which can be noticed as:
-
Lack of tears
-
Sunken eyes
-
Dark urine
-
Decrease in the frequency of urination
-
No wet diapers for 4-6 hours (infants and toddlers)
Causes Of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
HFMD is a viral infection that is caused by enterovirus family which includes mainly three viruses:
-
Coxsackievirus A16: It is the most common cause of HFMD.
-
Coxsackievirus A6: It is associated with the severe form of infection.
-
Enterovirus 71 (EV-A71): It is rarely found but is associated with severe diseases such as encephalitis
Transmission
The disease is highly contagious and can spread from one person to another through infected saliva, nasal secretions, fluid from blisters, and feces.
Usually, the chances of spreading the infection are high during the first 5 days of onset of symptoms. However, in some cases, infection can be spread even in the absence of symptoms or a little later due to the presence of virus in the stool for 4 to 8 weeks.
Anyone can get the disease by:
-
Contact with respiratory secretions during coughing or sneezing
-
Making close contact with the infected person such as during kissing, hugging, etc.
-
Touching an infected person
-
Sharing contaminated objects with the infected person
-
Touching an infected person’s feces such as during changing diapers
-
Touching the contaminated objects and surfaces such as doorknobs and toys
Note: In rare cases, the virus of HFMD can also be transmitted by swallowing water in swimming pools. This can happen, if the water is contaminated with feces of the infected person.
Risk Factors For Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Age
HFMD majorly affects infants and young children. Children less than 5 years are more prone to be infected by HFMD.
Gender
Some studies suggest that males are at higher risk of catching HFMD infection.
Poor hygiene
Since viruses that cause HFMD can live on surfaces and objects for some time, inadequate cleanliness increases the risk of HFMD.
High frequency of social contacts
Children who are regularly exposed to crowded places had greater risk of contracting the disease. These include school going children, children who play in the parks, children at the child-care center etc.
Sharing toys with other children
The toys can be contaminated by sharing with other children. This increases the risk of HFMD.
Residence in rural areas
Some studies suggest that children living in rural areas are more likely to catch HFMD infection due to more exposure to people.
Improper hand washing
The people who do not have a habit of washing their hands especially before meals and after using the toilet are at high risk of HFMD.
Note: HFMD is mild and self limiting. However, in some cases patients can develop severe neurological complications.
The risk factors that predisposes the person to severe HFMD include:
-
Infection in children of age less than 3 years
-
Fever or more than 3 days
-
Body temperature greater than 39.0°C
-
Vomiting
-
Increase neutrophil count
-
Respiratory rate greater than 24/minute
-
Trembling of limbs
-
Dyspnea (difficulty in breathing)
-
Rashes on hips
-
Lethargy
-
Convulsions
-
EV71 infection
-
Low birth weight
Diagnosis Of Hand,Foot, and Mouth Disease
The diagnosis of hand, foot, and mouth disease is usually simple. In the majority of cases, the diagnosis is made through examining the appearance of rashes, mouth ulcers, and blisters. The patient’s age and other clinical symptoms are also considered before confirming the infection. In some cases, samples of throat and feces are also examined.
Other tests that are rarely used include:
-
Biopsy: In this, the tissue taken from the vesicles of blisters is examined through light microscopy. It is done to differentiate hand, foot, and mouth disease from varicella zoster virus and herpes simplex virus.
-
Serological testing: Generally, this test is performed to confirm any viral infection through detecting antibodies. But, this test is not sensitive to make a diagnosis of HFMD virus. However, the test is used to monitor recovery through checking IgG levels.
-
Polymerase chain reaction: It is used to confirm the diagnosis of coxsackievirus.
Specialist To Visit
Although HFMD is usually a mild disease, any symptom should not be ignored as it can lead to several complications.
Consult the doctor if your child:
-
Has symptoms which are not improving even after 7 days
-
Is dehydrated due to inability to drink normally
-
Has pus around the sores
-
Finds it very difficult to wake up
-
Is not eating anything
-
Is always feeling irritated
-
Has a very high fever
Here are the things that can be done, if your child gets a fever.
You can consult the following doctors for proper diagnosis:
-
General physician
-
Pediatrician
-
Infectious disease specialist
Prevention Of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
There is no vaccine for hand, foot, and mouth disease but it can be easily prevented by following some basic steps which include:
-
Hand washing
Since, HFMD is a contagious disease that can spread through touching, hand washing serves the best protection. Hands should be washed often with soap and water and children should be educated about the importance of hand hygiene.
In case, soap and water are not available such as during traveling, alcohol based sanitizer can be used. Make sure to wash hands after:
-
Changing diapers
-
Using the toilet
-
Touching nose
-
Coughing and sneezing
-
Taking care of sick people
-
Cleaning and disinfection
The virus causing HFMD can live on surfaces for some time. It is advised to clean frequently touched surfaces and objects regularly such as toys, doorknobs, sippers, etc. Make sure to wash the soiled bedding and clothes with hot soap water.
-
Avoid touching eyes, nose and mouth
The infection can spread by touching eyes, nose, and mouth with contaminated hands. To reduce this, avoid touching eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands.
-
Avoid close contact with infected person
The disease can spread through close contact with the infected person especially during kissing, hugging, etc.
-
Avoid sharing of articles
Since the virus can live on objects for a few days, avoid sharing toys, towels, or household items such as cups and utensils of your kid with anyone. The regular cleaning of the shared toys and books should be practiced in childcare centers.
-
Stay off school or nursery
The spread of infection can be prevented by keeping kids home for a few days, especially if they have symptoms such as fever, blisters, or mouth ulcers.
-
Use tissues
Try not to cough or sneeze in the open air, always use tissue while doing the same. Make sure to dispose of the used tissues immediately to reduce the risk of infection.
Note: Breastfeeding does not impact the incidence of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Mothers do not need to stop breastfeeding to prevent transmission of disease.
Treatment Of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
There is no specific treatment for HFMD and children usually recover within 7 to 10 days on their own. As HFMD is a viral disease, antibiotics are not effective in curing the infection. The measures are taken to reduce symptoms and to prevent dehydration.
There are various studies that are going on to develop antiviral treatment against enterovirus 71 induced hand, foot, and mouth disease because of its neurological complications.
The following treatment regimen is used to treat HFMD:
-
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications such as paracetamol and ibuprofen are used to treat fever and pain caused by mouth sores.
-
The child does not want to have much fluids due to painful sores so proper hydration of the child should be maintained by making him/her to drink enough fluids.
-
A mixture of liquid ibuprofen and diphenhydramine can be used to gargle to reduce the pain caused by the ulcers.
-
Ribavirin, quinacrine, and amantadine are the off-label antiviral medications that are used in severe cases of enterovirus 71.
-
As per some studies, an antiviral drug, acyclovir showed the reduction in fever and skin changes within 24 hours of administration.
-
In case of severe dehydration and neurological or cardiopulmonary complications, hospitalization is required.
Note: Aspirin is not recommended in children since it is linked with a life threatning disorder called Reye’s syndrome which is a rare and potentially fatal pediatric illness. The syndrome causes serious liver and brain damage. The disease typically presents as vomiting and confusion which can even lead to coma and death.
Tips to soothe sore throat
-
Throat lozenges and sprays that do not contain benzocaine can be used for children over 4 years of age.
-
Liquid antacid can be used for rinsing after meals.
-
Garling with a mixture of warm water and salt is very effective in children over 6 years of age who are able to gargle without swallowing.
Home-care For Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Although the disease is mild and usually goes away on its own, the symptoms such as painful mouth sores make it very difficult for the child to eat and drink. This makes the child even more irritable and fussy.
The parents of the sick child should understand that the child will not be able to eat much for at least 7 to 10 days. It is advised that parents should shift the child from solid to soft liquids.
The following measures may help in faster recovery of the child:
Diet
- Foods to include- The child should be encouraged to have fluids such as water, milk, coconut water to prevent dehydration. The cold and soft foods such as ice cream, yogurt, smoothies, shakes, mashed potatoes, oatmeal, eggs, and popsicles should be included in the diet as it will help in numbing the area. This will not only serve as a welcome treat for kids but also soothes the ulcers.
- Foods to avoid- The acidic food items (citrus juices, lemonade, sodas and tomato sauces) can irritate the mouth sores and hence should be avoided. It is recommended to avoid hot drinks and spicy foods as they can aggravate the pain caused by mouth sores.
Cleaning of blisters
The blisters that usually appear on hands and feet should be kept clean through regular washing with soap and water. In case, the blisters rupture, they should be cleaned with an antibiotic ointment to prevent any infection.
Avoidance of self medication
There are various OTC medications that can harm infants and young children. Avoid giving any medication without the paeditrician’s consent to your child.
Education
The child should be taught not to touch the rash and mouth ulcers and to sneeze or cough into a tissue or on his/her sleeve. Education of hand hygiene is equally important.
Staying at home
The day care centers and schools of the child should be informed that he/she is diagnosed with the HFMD. It is important to inform staff and parents so that they can watch symptoms in other children. The child should be kept at home until the full recovery of mouth sores and open blisters.
Breastfeeding
If your child is under one year old, continue to give either breastmilk, formula, or both.
Complications Of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
The disease is acute with mild symptoms. Most of the patients of HFMD recover within a few weeks and the infection rarely recurs or persists. The complications from hand, foot, and mouth disease are rare and include:
Dehydration
It is the most common complication associated with HFMD. Children often get dehydrated due to difficulty in swallowing as a result of painful mouth ulcers. Hence, it has to be made sure to maintain optimum hydration.
Here are some basic tips that can be done, if you are feeling dehydrated.
Persistent stomatitis
It refers to the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth. It is often associated with painful ulcers that limit intake of food.
Aseptic (viral) meningitis
It refers to the inflammation of the layers of the brain due to viral infection. It is more common with enterovirus 71 infection. It is often characterized by fever, headache, stiff neck, or back pain.
Fingernail and toenail loss
In very severe cases, people may start losing fingernail or toenail which is usually noticed after 2 months of having an infection. The nail usually grows back on its own.
In severe cases of infection, HFMD can also cause:
-
Widespread rash
-
Enteritis (Infection of the gut)
-
Myocarditis (inflammation of the muscle of the heart)
-
Pulmonary edema (accumulation of fluids in the lungs)
-
Cerebral ataxia (sudden, uncoordinated muscle movement due to injury to the brain)
-
Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
-
Guillain-Barre syndrome (a rare disorder in which your body's immune system attacks your nerves)
-
Intracranial hypertension (build-up of pressure around the brain)
-
Paralysis
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in Pregnancy
Although there is no potential risk to the baby and mother, the medical history of the patient can affect the situation. Pregnant women should contact the doctor as in rare cases, HFMD can lead to misscarriage during the first trimester due to persistent high temperature.
Note: HFMD can affect adults also. But, most infected adults do not seem to show any symptoms, they are, however, still contagious and can spread the virus to another person.
Alternative Therapies For Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Home remedies
1. Coconut water: Coconut water acts as a coolant and contains vitamins, minerals, electrolytes and antioxidants. It prevents dehydration and also helps in reducing the mouth pain.
2. Oil pulling: It is an old method of maintaining good oral hygiene and involves swishing any oil such as sesame or coconut in the mouth for 5 to 10 minutes. It helps in soothing the mouth sores.
3. Cod liver oil: It serves as a very good remedy for HFMD due to its antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties. It can be given in the form of capsules available in the market or by mixing it in oil or yogurt.
4. Echinacea: It is a herb that is known to reduce fever, cold, and infections. It can be prepared by boiling its leaves in water and adding honey to it.
5. Lavender oil: It is known for its antiviral properties. It also has a calming and relaxing effect which aids in sleep. A few drops of this oil in the bath water help your child to sleep better.
6. Liquorice root: Liquorice root can help to soothe blisters by forming a thin layer of mucous inside the throat and esophagus. It can be taken in the form of tea prepared by boiling some liquorice roots in water.
7. Ginger: Ginger is also one of the effective home remedies as it has antiviral properties. It can be prepared by boiling chopped ginger in water. Make sure to cool it before giving it to your child.
8.Coconut oil: Coconut oil can be applied on the rashes and blisters for a soothing and healing effect.
9. Neem: It has antimicrobial properties and is mostly used topically to treat viral infections. Neem oil can be applied on the rashes. It can also be used with coconut oil and lavender oil.
10. Aloe-vera: The gel of aloe vera can be applied on the rashes and blisters for soothing relief.
Frequently Asked Questions
References
- Saguil A, Kane SF, Lauters R, Mercado MG. Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease: Rapid Evidence Review. Am Fam Physician. 2019 Oct 1;100(7):408-414. PMID: 31573162.
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, World Health Organization.
- Cox B, Levent F. Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease. JAMA. 2018;320(23):2492. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.17288.
- Guerra AM, Orille E, Waseem M. Hand Foot And Mouth Disease. [Updated 2022 May 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan.
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, Center Of Disease Control and Prevention, Last Updated On: February 02, 2021.
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, NHS, Last Updated On: February 12, 2021.
- Kua JA, Pang J. The epidemiological risk factors of hand, foot, mouth disease among children in Singapore: A retrospective case-control study. PLoS One. 2020 Aug 11;15(8):e0236711. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236711. PMID: 32780749; PMCID: PMC7418981.