Pittapapada
Pittapapada
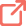
Pittapapada or Fumitory is an annual herb found as a common weed all over the plains of India. The whole plant is widely used in traditional and folkloric systems of medicine. In traditional systems of medicine, the plant is reputed for its anthelmintic, diuretic, diaphoretic, laxative, cholagogue, stomachic, sedative, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, analgesic, prokinetic, laxative, dermatological, antimicrobial, antiparasitic, reproductive, anticholinesterase, and smooth muscle relaxant effects. These properties help to manage diseases like dyspepsia and scrofulous skin infection, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, fever, jaundice, leprosy, and syphilis. The plant is also used to purify blood in cutaneous disease and liver obstruction[2][3].
What are the synonyms of Pittapapada?
Fumaria parviflora, Varatika, Suksmapatra, Shahtaraj, Vanshulpha, Bansulpha, Pitpapado, Pittapapado, Dhamgajra, Pittapapara, Kallu Sabbasige, Parpatu, Chaturasigide, Shatara, Parpat, Shahtara, Pittapapara, Tura, Tusa, Parpatakamu, Parpata[1].
What is the source of Pittapapada?
Plant Based
Benefits of Pittapapada
1. Diarrhea
Diarrhea is known as Atisar in Ayurveda. It occurs due to improper food, impure water, toxins, mental stress and Agnimandya (weak digestive fire). All these factors are responsible for aggravating Vata. This aggravated Vata brings fluid to the intestines from various tissues of the body and mixes with the stool which leads to loose, watery motions or Diarrhea. Pittapapada helps in the management of Diarrhea due to its Grahi (absorbent) property. It helps absorb the excessive loss of water and reduces the frequency of watery stools.
2. Anorexia
Due to low digestive fire (Mand agni), the ingested food might not get digested properly, resulting in the formation of Ama (toxic remains in the body due to improper digestion). This might lead to anorexia or loss of appetite, also known as Aruchi in Ayurveda. It is a condition which results in the imbalance of Vata, Pitta and Kapha doshas. There are also some psychological factors that lead to incomplete digestion of food, causing insufficient secretion of gastric juice in the stomach, thereby resulting in loss of appetite. Pittapapada helps in the management of anorexia due to its Pitta-Kapha balancing properties. This helps prevent the formation of Ama and improves the taste due to its Rochaka (taste enhancer) property which further reduces anorexia.
3. Vomiting
Vomiting occurs due to an imbalance of all three doshas, especially Pitta and Kapha dosha. Doshas get imbalanced due to various eating habits like consuming food that is excessive Teekshna (sharp), Kashaya (pungent), Amla (sour), Vidahi (which causes burning sensation), Guru (heavy), Ati-Sheeta (cold) and Apakwa Ahaara (raw/uncooked) in nature. This results in the formation of Ama (toxic remains in the body due to improper digestion) leading to indigestion. Pittapapada helps manage Vomiting by reducing Ama and improving digestion due to it’s Pitta and Kapha balancing properties properties.
4. Indigestion
According to Ayurveda, Indigestion is termed as Agnimandya. It occurs due to an imbalance of Pitta dosha. Whenever the ingested food is left undigested due to Mand agni (low digestive fire), it results in the formation of Ama (toxic remains in the body due to improper digestion) and causes indigestion. Pittapapada helps improve taste which enhances the Agni, thus leading to an improved digestion due to its Pitta balancing and Rochaka (taste enhancer) properties.
Diarrhea is known as Atisar in Ayurveda. It occurs due to improper food, impure water, toxins, mental stress and Agnimandya (weak digestive fire). All these factors are responsible for aggravating Vata. This aggravated Vata brings fluid to the intestines from various tissues of the body and mixes with the stool which leads to loose, watery motions or Diarrhea. Pittapapada helps in the management of Diarrhea due to its Grahi (absorbent) property. It helps absorb the excessive loss of water and reduces the frequency of watery stools.
2. Anorexia
Due to low digestive fire (Mand agni), the ingested food might not get digested properly, resulting in the formation of Ama (toxic remains in the body due to improper digestion). This might lead to anorexia or loss of appetite, also known as Aruchi in Ayurveda. It is a condition which results in the imbalance of Vata, Pitta and Kapha doshas. There are also some psychological factors that lead to incomplete digestion of food, causing insufficient secretion of gastric juice in the stomach, thereby resulting in loss of appetite. Pittapapada helps in the management of anorexia due to its Pitta-Kapha balancing properties. This helps prevent the formation of Ama and improves the taste due to its Rochaka (taste enhancer) property which further reduces anorexia.
3. Vomiting
Vomiting occurs due to an imbalance of all three doshas, especially Pitta and Kapha dosha. Doshas get imbalanced due to various eating habits like consuming food that is excessive Teekshna (sharp), Kashaya (pungent), Amla (sour), Vidahi (which causes burning sensation), Guru (heavy), Ati-Sheeta (cold) and Apakwa Ahaara (raw/uncooked) in nature. This results in the formation of Ama (toxic remains in the body due to improper digestion) leading to indigestion. Pittapapada helps manage Vomiting by reducing Ama and improving digestion due to it’s Pitta and Kapha balancing properties properties.
4. Indigestion
According to Ayurveda, Indigestion is termed as Agnimandya. It occurs due to an imbalance of Pitta dosha. Whenever the ingested food is left undigested due to Mand agni (low digestive fire), it results in the formation of Ama (toxic remains in the body due to improper digestion) and causes indigestion. Pittapapada helps improve taste which enhances the Agni, thus leading to an improved digestion due to its Pitta balancing and Rochaka (taste enhancer) properties.
Precautions when using Pittapapada
Breastfeeding

Modern Science View
Since enough scientific evidence is not available, it is advisable to avoid or consult a physician before taking Pittapapada during breastfeeding.
Patients with diabetes

Modern Science View
Since enough scientific evidence is not available, it is advisable for diabetics to avoid or consult a physician before taking Pittapapada.
Patients with heart disease

Modern Science View
Since enough scientific evidence is not available, it is advisable for patients with heart disease to avoid or consult a physician before taking Pittapapada.
Patients with liver disease

Modern Science View
Long term exposure to low doses of Pittapapada may cause certain harm to hepatic (liver) tissues. So it is advisable for patients with liver disease to avoid or consult a physician before using Pittapapada[12].
Pregnancy

Modern Science View
Since enough scientific evidence is not available, it is advisable to avoid or consult a physician before taking Pittapapada during pregnancy.
Recommended Dosage of Pittapapada
- Pittapapada Powder - ½ - 1 teaspoon, 1-2 times a day.
How to use Pittapapada
1. Pittapapada Powder
a. Take ½ - 1 teaspoon of Pittapapada powder.
b. Swallow it with lukewarm water 1-2 times a day.
c. Repeat regularly to improve good digestion.
2. Pittapapada Decoction
a. Take 10-20 teaspoon of Pittapapada Decoction.
b. Add the same quantity of water to it.
c. Drink it preferably in the morning 1-2 times a day.
d. Repeat regularly to get relief from diarrhea.
a. Take ½ - 1 teaspoon of Pittapapada powder.
b. Swallow it with lukewarm water 1-2 times a day.
c. Repeat regularly to improve good digestion.
2. Pittapapada Decoction
a. Take 10-20 teaspoon of Pittapapada Decoction.
b. Add the same quantity of water to it.
c. Drink it preferably in the morning 1-2 times a day.
d. Repeat regularly to get relief from diarrhea.
Frequently asked questions

Modern Science View
The extract of Pittapapada should be sealed in an aluminium foil and stored at 4 degrees celsius.
References
- The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia Of India.Part 1 Volume 1.
Disclaimer
The content is purely informative and educational in nature and should not be construed as medical advice. Please use the content only in consultation with an appropriate certified medical or healthcare professional.